To provide a bit of historical context for our recent posts on infrastructure costs (see here and here), check out this piece from Scientific American in 1907.
The cover of the issue (comparing the NYC skyline to Niagara and Victoria Falls ) has nothing to do with this, but it's still pretty cool.
Comments, observations and thoughts from two bloggers on applied statistics, higher education and epidemiology. Joseph is an associate professor. Mark is a professional statistician and former math teacher.
Wednesday, February 14, 2018
Tuesday, February 13, 2018
“I’m almost afraid not to take the chance,” – This is when it becomes a bubble.
It's that moment when risk aversion flips and the thought of not making money starts to feel like losing it. I'm not talking about opportunity costs in any kind of rational sense. Instead, I'm referring to having the visceral emotional reaction associated with a deep, costly loss because you didn't buy into the skyrocketing market the day before. People become afraid not to invest in what should obviously be highly risky ventures.
Truly crazy bubbles are driven by this paradoxical combination of greed and fear. They both desire instant wealth and dread the sense of regret that would go with missing it. Individually, either of these emotions can drive otherwise sensible people into irrational behavior. Together, they can spur investment in some laughably bad ideas.
This Washington Post piece by Chico Harlan on a group of Bitcoin investors perfectly illustrates the point.
“Us little guys working our butts off, we can’t get ahead,” Cedric Knight, 35, told Melin. “This is a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to change my life.”
Knight and others visiting Melin were pinning their hopes on a new form of currency whose potential value the world was only beginning to recognize. Millions of people around the world are chasing after fortune by investing in bitcoin — which has soared by more than 2,500 percent in value in the past two years — and other digital instruments known as cryptocurrencies.
...
“What crypto allows is for the masses to be venture capitalists,” Melin said.
“And guys like me, I’m not in the loop,” Knight said. “This is my chance.”
…
Knight, meantime, went home, cooked dinner and then decided to reopen one of the eight cryptocurrency apps he had downloaded. His account had fallen nearly $500 on the day — his initial $1,500 was below $900 — and he said he was “freaking out.” But then, he thought about what it meant to be a cryptocurrency investor. There would be days such as this. But there might be better days, too — much better days. If there were, he did not want to miss out.
“I’m almost afraid not to take the chance,” he said, and soon, he added $260 to his cryptocurrency account.
Some historical perspective from the archives.
"A company for carrying on an undertaking of great advantage, but nobody to know what it is."
Another except from Charles Mackay's Extraordinary Popular Delusions and the Madness of Crowds. I believe "a company for carrying on an undertaking of great advantage, but nobody to know what it is" was an initial business plan for Groupon.Some of these schemes were plausible enough, and, had they been undertaken at a time when the public mind was unexcited, might have been pursued with advantage to all concerned. But they were established merely with the view of raising the shares in the market. The projectors took the first opportunity of a rise to sell out, and next morning the scheme was at an end. Maitland, in his History of London, gravely informs us, that one of the projects which received great encouragement, was for the establishment of a company "to make deal-boards out of saw-dust." This is, no doubt, intended as a joke; but there is abundance of evidence to show that dozens of schemes hardly a whir more reasonable, lived their little day, ruining hundreds ere they fell. One of them was for a wheel for perpetual motion—capital, one million; another was "for encouraging the breed of horses in England, and improving of glebe and church lands, and repairing and rebuilding parsonage and vicarage houses." Why the clergy, who were so mainly interested in the latter clause, should have taken so much interest in the first, is only to be explained on the supposition that the scheme was projected by a knot of the foxhunting parsons, once so common in England. The shares of this company were rapidly subscribed for. But the most absurd and preposterous of all, and which showed, more completely than any other, the utter madness of the people, was one, started by an unknown adventurer, entitled "company for carrying on an undertaking of great advantage, but nobody to know what it is." Were not the fact stated by scores of credible witnesses, it would be impossible to believe that any person could have been duped by such a project. The man of genius who essayed this bold and successful inroad upon public credulity, merely stated in his prospectus that the required capital was half a million, in five thousand shares of 100 pounds each, deposit 2 pounds per share. Each subscriber, paying his deposit, would be entitled to 100 pounds per annum per share. How this immense profit was to be obtained, he did not condescend to inform them at that time, but promised, that in a month full particulars should be duly announced, and a call made for the remaining 98 pounds of the subscription. Next morning, at nine o'clock, this great man opened an office in Cornhill. Crowds of people beset his door, and when he shut up at three o'clock, he found that no less than one thousand shares had been subscribed for, and the deposits paid. He was thus, in five hours, the winner of 2,000 pounds. He was philosopher enough to be contented with his venture, and set off the same evening for the Continent. He was never heard of again
Monday, February 12, 2018
Laws and markets
This is Joseph
This point, by James Joyner, is quite good:
But all markets are based on rules and laws. We would have no markets at all if force and fraud where not prohibited, for example. The piece that is dodgy here is the evasion of the existing rules in order to build a company. It is fine to lobby to change the rules. But when you have to design your business to evade local regulations then that is a problem. Not because the laws are good -- they are likely not. But because it is not the case that private actors who violate laws that they see as stifling innovation are left alone.
And if government is wrong about a law and needs to backtrack then it makes sense to compensate the losers of the law change. We don't let private property block roads but we do have to buy it back when we put a road in. I think applying the same logic to shutting down taxi licensing agreements is sensible.
This point, by James Joyner, is quite good:
The taxi industry is a special case, though, in that cab and limousine owners and drivers made economic decisions based on rules set by the government. While the medallion system is outrageous and I’m happy to see it disrupted, the fact of the matter is that it was the norm for generations. People saved up or took big risks in borrowing to bid on them based on guarantees from their municipal government. They have every right to expect that same government to either enforce the law against illegal competition or compensate them in some way for the broken contract.The piece that is very important here is the decision to change the legal framework. Disruption is normal and many people end up as economic losers when conditions change. We are already bad at coping with that.
But all markets are based on rules and laws. We would have no markets at all if force and fraud where not prohibited, for example. The piece that is dodgy here is the evasion of the existing rules in order to build a company. It is fine to lobby to change the rules. But when you have to design your business to evade local regulations then that is a problem. Not because the laws are good -- they are likely not. But because it is not the case that private actors who violate laws that they see as stifling innovation are left alone.
And if government is wrong about a law and needs to backtrack then it makes sense to compensate the losers of the law change. We don't let private property block roads but we do have to buy it back when we put a road in. I think applying the same logic to shutting down taxi licensing agreements is sensible.
Friday, February 9, 2018
The Snow Bicycle -- wonder why this never caught on
People at the turn of the century were fascinated by the bicycle, both as a practical form of transportation and as a sport. Being an age of great inventiveness, lots of variations were tried, some more viable than others.
I've been working on a project involving not only the technological explosion of the late 19th and early 20th Centuries (which introduced the huge hit Daisy Bell)...
... but also the post-war period (where the still remembered Daisy Bell would provide and interesting footnote).
Which inspired...
I've been working on a project involving not only the technological explosion of the late 19th and early 20th Centuries (which introduced the huge hit Daisy Bell)...
... but also the post-war period (where the still remembered Daisy Bell would provide and interesting footnote).
Which inspired...
Thursday, February 8, 2018
That New York Times piece on Tesla was even worse than I thought.
In case you missed part one,a few days ago, I took John F. Wasik and the New York Times to task for a piece that attempted to mythologize Nikola Tesla by distorting the historical record and omitting a number of pertinent facts. One passage I jumped on somewhat vigorously was the following.
Tesla proposed the development of torpedoes well before World War I. These weapons eventually emerged in another form — launched from submarines.
I pointed out that there was no way Tesla could have "proposed" the development of torpedoes in the late 1890s since the Whitehead self-propelled torpedo had been in use for decades and had already revolutionized naval warfare. What I failed to catch was just how off the second sentence was. I knew that the "eventually" was stretching it, but I didn't realize that it wasn't even directionally accurate.
Submarines were another line of technology that made revolutionary leaps due to advances in internal combustion and electricity. It turns out that there were a number of torpedo-firing subs being tested and even, to a limited extent, deployed by the time that Tesla demonstrated his torpedo. We can probably dismiss the first submarine to fire a torpedo while submerged (way back in 1886) as a failed experiment, but by the late 1890s, viable models were in the water, most notably the USS Holland which established most of the main features (albeit in a simplified form) of submarines until the advent of nuclear power.
[In addition to torpedoes, the boat was armed with a pneumatic dynamite gun seen here.]
I realize I'm piling on, but there's a lot of wrong here, and seeing the facts so badly mangled in the New York Times, a publication that prides itself on fact checking, raises serious questions. I'd offer a couple of possible explanations. First, I suspect a great deal of the push for accuracy is driven by fear of how subjects might react. Writing about people long dead takes a certain amount of the pressure off.
Second, and I think more important, the lone, misunderstood visionary is a popular and reassuring conventional narrative. It tells a good story and it makes us feel superior to the people of Tesla's time (we, being sophisticated and having a deep understanding of technology, would have immediately seen the potential of these ideas). Lord Keynes famously said “Worldly wisdom teaches that it is better for reputation to fail conventionally than to succeed unconventionally.” The journalistic corollary of that is that standards are lower if you stick to conventional narratives and approved memes. Alessandra Stanley can prompt corrections that threaten to go on longer than the original articles. Maureen Dowd can babble incoherently about Washington dinner party gossip. David Brooks can simply make shit up. It's all okay because they are telling familiar stories that the establishment is comfortable with. The knives only come out for independent thought.
Wednesday, February 7, 2018
“One of the most powerful influences for broadening human intelligence… has spread an even, highly developed civilization through the land… has unified the Nation.”
From an AT&T advertisement that ran in Scientific American. June 19th, 1909.
Even allowing for the inevitable hyperbole of ad copy, this is big talk, but it is highly indicative of its era. There was a widespread, perhaps even dominant belief among turn-of-the-century Americans that the generation of unprecedented technological progress they had just witnessed marked the beginning of a new age of civilization and perhaps even human evolution.
This was about the time that the idea of and unimaginable future coming at us with ever-increasing speed first took hold in the public consciousness. It was also perhaps the last time events justified the notion.
Even allowing for the inevitable hyperbole of ad copy, this is big talk, but it is highly indicative of its era. There was a widespread, perhaps even dominant belief among turn-of-the-century Americans that the generation of unprecedented technological progress they had just witnessed marked the beginning of a new age of civilization and perhaps even human evolution.
This was about the time that the idea of and unimaginable future coming at us with ever-increasing speed first took hold in the public consciousness. It was also perhaps the last time events justified the notion.
Tuesday, February 6, 2018
"It’s not just the Second Avenue Subway"
Over at Citylab, Alon Levy has a great piece on the costs of passenger rail.
The approximate range of underground rail construction costs in continental Europe and Japan is between $100 million per mile, at the lowest end, and $1 billion at the highest. Most subway lines cluster in the range of $200 million to $500 million per mile; in Amsterdam, a six-mile subway line cost 3.1 billion Euros, or about $4 billion, after severe cost overruns, delays, and damage to nearby buildings. The Second Avenue Subway is unique even in the U.S. for its exceptionally high cost, but elsewhere, the picture is grim by European standards:
It is hard to find exact international comparisons for subway lines running in the medians of freeways. However, it should not be much more difficult to construct such lines than to build light rail. Indeed, in the study for Atlanta’s I-20 East extension, there are options for light rail and bus rapid transit, and the light rail option is only slightly cheaper than the heavy rail option, at $140 million per mile.
Line Type Cost Length Cost/mile San Francisco Central Subway Underground $1.57 billion 1.7 miles $920 million Los Angeles Regional Connector Underground $1.75 billion 1.9 miles $920 million Los Angeles Purple Line Phases 1-2 Underground $5.2 billion 6.5 miles $800 million BART to San Jose (proposed) 83% Underground $4.7 billion 6 miles $780 million Seattle U-Link Underground $1.8 billion 3 miles $600 million Honolulu Area Rapid Transit Elevated $10 billion 20 miles $500 million Boston Green Line Extension Trench $2.3 billion 4.7 miles $490 million Washington Metro Silver Line Phase 2 Freeway median $2.8 billion 11.5 miles $240 million Atlanta I-20 East Heavy Rail Freeway median $3.2 billion 19.2 miles $170 million
Lists of light-rail lines built in France in recent years can be found on French Wikipedia and Yonah Freemark’s The Transport Politic, and in articles in French media. The cheaper lines cost about $40 million per mile, the more expensive ones about $100 million.
In the United States, most recent and in-progress light-rail lines cost more than $100 million per mile. Two light-rail extensions in Minneapolis, the Blue Line Extension and the Southwest LRT, cost $120 million and $130 million per mile, respectively. Dallas’ Orange Line light rail, 14 miles long, cost somewhere between $1.3 billion and $1.8 billion. Portland’s Orange Line cost about $200 million per mile. Houston’s Green and Purple Lines together cost $1.3 billion for about 10 miles of light rail.
Monday, February 5, 2018
This is almost beyond parody
This is Joseph
From Duncan Black, we have this article:
Second, there is a huge implicit road subsidy here for these companies, presuming non-AVs would need to be banned as well. Roads that can only be used by corporations (not individuals) that appear to be supported by public taxation.
Three, doesn't this create perverse incentives to make public transportation less effective, via lobbying for weaker bus service, especially if AVs become more standard?
Four, isn't regulation intended to give private benefit to a public good a problem? Allowing an AV to only be operated by a collective seems to be an odd regulation. In what other area do we restrict items to use by corporations but ban private use? There must be some but . . .
Five, doesn't this likely end up with more non-AVs on the road, making the AVs less safe because they can't communicate with non-AVs?
It seems like a very self-serving idea as a ride sharing fleet. I am curious what benefits we have here that wouldn't apply to public transit?
From Duncan Black, we have this article:
And today, a coalition of companies—including Lyft, Uber, and Zipcar—officially announced that they were signing on to a 10-point set of “shared mobility principles for livable cities”—in other words, industry goals for making city transit infrastructure as pleasant, equitable, and clean as possible. Some of the 10 statements, like “we support people over vehicles,” are vague but positive. But the final one speaks loudly about what city roads of the future could look like: “that autonomous vehicles (AVs) in dense urban areas should be operated only in shared fleets.”
It’s a “very convenient” idea for the companies who are promoting it, says Don MacKenzie, an assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering at the University of Washington. “It is basically [tying] the success of these companies to the adoption of autonomous vehicles,” he says. In other words, putting this principle in action means that “if people want the benefits of AVs, they can only get that by using shared fleets.” (Worth noting that the concept only applies to dense urban areas.)Ok, the first thing here is that any possible argument for this approach for AVs is going to apply to public transit as well. Bus service would be greatly improved if many or most cars were banned or restricted from operation on city streets.
Second, there is a huge implicit road subsidy here for these companies, presuming non-AVs would need to be banned as well. Roads that can only be used by corporations (not individuals) that appear to be supported by public taxation.
Three, doesn't this create perverse incentives to make public transportation less effective, via lobbying for weaker bus service, especially if AVs become more standard?
Four, isn't regulation intended to give private benefit to a public good a problem? Allowing an AV to only be operated by a collective seems to be an odd regulation. In what other area do we restrict items to use by corporations but ban private use? There must be some but . . .
Five, doesn't this likely end up with more non-AVs on the road, making the AVs less safe because they can't communicate with non-AVs?
It seems like a very self-serving idea as a ride sharing fleet. I am curious what benefits we have here that wouldn't apply to public transit?
Friday, February 2, 2018
I think Uber might be using the hover-plane design for its proposed flying taxis.
As we mentioned before, fairly early in the 20th century, popular culture seem to have settled on the period roughly around 1890 as the end of the simple, leisurely-paced good old days, just before technological revolution sent the country hurtling into the future.
Just Imagine is a good example if not a good film (to be perfectly honest, I've never made it all the way through without skipping sizable chunks). The period of comparison is pushed back to 1880 – – probably in order to have a nice round hundred years before the main action set in 1980 – – but the rest of the formula is there.
El (short for Elmer) Brendel was a popular Swedish dialect comedian who was popular at the time (though not popular enough for either of his starring vehicles to turn a profit). These days he is remembered almost solely for this film which itself is remembered mainly for providing stock footage for Saturday morning serials like Flash Gordon and Buck Rogers.
It's worth checking out the first few minutes just for the art direction and then fast forwarding to around the 22 minute mark where Henry Ford's anti-Semitism provides the subject for a then topical joke.
Just Imagine is a good example if not a good film (to be perfectly honest, I've never made it all the way through without skipping sizable chunks). The period of comparison is pushed back to 1880 – – probably in order to have a nice round hundred years before the main action set in 1980 – – but the rest of the formula is there.
El (short for Elmer) Brendel was a popular Swedish dialect comedian who was popular at the time (though not popular enough for either of his starring vehicles to turn a profit). These days he is remembered almost solely for this film which itself is remembered mainly for providing stock footage for Saturday morning serials like Flash Gordon and Buck Rogers.
It's worth checking out the first few minutes just for the art direction and then fast forwarding to around the 22 minute mark where Henry Ford's anti-Semitism provides the subject for a then topical joke.
Thursday, February 1, 2018
Media Post: Game of Thrones and succession
This is Joseph
** SPOILERS**
As some readers may know, the TV show game of thrones has bypassed the book series a song of ice and fire by George RR Martin. In the process, they have also appeared to merge a number of characters together, to reduce complexity. In the process, however, they have undermined a key piece of the entire story.
The plot that starts the whole series off is the discovery that the children of Cersei Lannister are not the real children of the king, Robert Baratheon. As a result, they lack a blood claim to the iron throne. In parallel, we have the story of Daenerys Targaryen who is seeking to reclaim the iron throne because she is a relative of the deposed king. We also have a history of a rebellion where the king was overthrown and replaced by a relative (said Robert) who had a close blood claim on the throne. Finally. there is a hidden twist where the bastard son of Ned Stark, Jon Snow, is actually the legitimate son of the Targaryen prince and has a stronger claim to the throne than Daenerys.
So the whole plot is driven by blood claims and how they influence character's succession rights. It is also a medieval world and not a modern one -- the king needs the support of the nobles in order to raises armies and funds. These nobles, themselves, depend on succession for legitimacy.
In the last season there were some questionable succession moves. But for some of them I can justify how the claim comes into being. Cersei Lannister is a close relative (mother) of the last king and happens to be in charge of the regency at the time. It's not typical, but it happened with Catherine the Great (for example) where a marriage/parentage claim allowed an unexpected monarch. Same with the Queen of Thorns -- she is at least a close relative of the last head of house Tyrell. An odd succession choice but you can see how she could have been a compromise candidate.
But what is going on with Ellaria Sand? She leads a coup to kill the members of the ruling family of Dorne. She is the illegitimate girlfriend of the brother of the previous ruler. How does she end up in charge? Now I could imagine a sand snake in charge -- they are also illegitimate but are at least the daughters of Oberyn Martell. But Ellaria?
Ellaria then joins forces with Daenerys, whose only legitimate claim on the iron throne rests on blood succession. If you take that away then you have a foreign invader pursuing a grudge against the family of people who wronged her (it is obvious that Cersei, herself, had nothing to do with Robert's Rebellion and the major rebels are all dead).
Why would Daenerys undermine the major point in her favor (succession law) by allying with somebody who has no succession rights to her current position (inside her kingdom) and, at the very least, was suspiciously involved with the violent death of the previous ruler and heir. I mean both were cut down along with their bodyguard -- nobody is dumb enough to think that this is an accident.
What I think happened was that they merged Arianne Martel with Ellaria. If Arianne did this plot then that would be different. Without clear evidence that she was the murderer then she has the best claim to the throne (being the current heir). Ambiguity might preserve her position (think of Edward II and Edward III) and objectors would have to act fast to gather evidence. Nobles wouldn't see their succession rights being tainted.
But this adaption definitely requires some more thought and should have been staged better. Why not put Obara Sand in charge, as the closet blood relative to the now extinct house of Martell? It might not be extinct in the books, but at least in the show that would be an easy claim to make as they killed every Martell we met. As it is, without additional information, the succession of Ellaria Sand to the leadership of Dorne undermines the main force driving the political plot and reduces the coherence of the story.
This was not one of the changes that improved the show.
** SPOILERS**
As some readers may know, the TV show game of thrones has bypassed the book series a song of ice and fire by George RR Martin. In the process, they have also appeared to merge a number of characters together, to reduce complexity. In the process, however, they have undermined a key piece of the entire story.
The plot that starts the whole series off is the discovery that the children of Cersei Lannister are not the real children of the king, Robert Baratheon. As a result, they lack a blood claim to the iron throne. In parallel, we have the story of Daenerys Targaryen who is seeking to reclaim the iron throne because she is a relative of the deposed king. We also have a history of a rebellion where the king was overthrown and replaced by a relative (said Robert) who had a close blood claim on the throne. Finally. there is a hidden twist where the bastard son of Ned Stark, Jon Snow, is actually the legitimate son of the Targaryen prince and has a stronger claim to the throne than Daenerys.
So the whole plot is driven by blood claims and how they influence character's succession rights. It is also a medieval world and not a modern one -- the king needs the support of the nobles in order to raises armies and funds. These nobles, themselves, depend on succession for legitimacy.
In the last season there were some questionable succession moves. But for some of them I can justify how the claim comes into being. Cersei Lannister is a close relative (mother) of the last king and happens to be in charge of the regency at the time. It's not typical, but it happened with Catherine the Great (for example) where a marriage/parentage claim allowed an unexpected monarch. Same with the Queen of Thorns -- she is at least a close relative of the last head of house Tyrell. An odd succession choice but you can see how she could have been a compromise candidate.
But what is going on with Ellaria Sand? She leads a coup to kill the members of the ruling family of Dorne. She is the illegitimate girlfriend of the brother of the previous ruler. How does she end up in charge? Now I could imagine a sand snake in charge -- they are also illegitimate but are at least the daughters of Oberyn Martell. But Ellaria?
Ellaria then joins forces with Daenerys, whose only legitimate claim on the iron throne rests on blood succession. If you take that away then you have a foreign invader pursuing a grudge against the family of people who wronged her (it is obvious that Cersei, herself, had nothing to do with Robert's Rebellion and the major rebels are all dead).
Why would Daenerys undermine the major point in her favor (succession law) by allying with somebody who has no succession rights to her current position (inside her kingdom) and, at the very least, was suspiciously involved with the violent death of the previous ruler and heir. I mean both were cut down along with their bodyguard -- nobody is dumb enough to think that this is an accident.
What I think happened was that they merged Arianne Martel with Ellaria. If Arianne did this plot then that would be different. Without clear evidence that she was the murderer then she has the best claim to the throne (being the current heir). Ambiguity might preserve her position (think of Edward II and Edward III) and objectors would have to act fast to gather evidence. Nobles wouldn't see their succession rights being tainted.
But this adaption definitely requires some more thought and should have been staged better. Why not put Obara Sand in charge, as the closet blood relative to the now extinct house of Martell? It might not be extinct in the books, but at least in the show that would be an easy claim to make as they killed every Martell we met. As it is, without additional information, the succession of Ellaria Sand to the leadership of Dorne undermines the main force driving the political plot and reduces the coherence of the story.
This was not one of the changes that improved the show.
Wednesday, January 31, 2018
Alon vs. Elon
Alon Levy is a highly respect transportation blogger currently based in Paris. He's also perhaps the leading debunker of the Hyperloop (or more accurately, the “Hyperloop,” but that's a topic we've probably exhausted). When Brad Plumer writing in the Washington Post declared ‘There is no redeeming feature of the Hyperloop.’, the headline was a quote from Levy.
Recently, Levy took a close look at Musk's Boring Company and found the name remarkably apt. We'd previously expressed skepticism about Musk's claim, but it turns out we were being way too kind.
Levy's takedown is detailed but readable and I highly recommend going through it if you have any interest in what drives infrastructure costs. Rather than try to excerpt some of the more technical passages, I thought I'd stick with the following general but still sharp observation from the post.
Recently, Levy took a close look at Musk's Boring Company and found the name remarkably apt. We'd previously expressed skepticism about Musk's claim, but it turns out we were being way too kind.
Levy's takedown is detailed but readable and I highly recommend going through it if you have any interest in what drives infrastructure costs. Rather than try to excerpt some of the more technical passages, I thought I'd stick with the following general but still sharp observation from the post.
Americans hate being behind. The form of right-wing populism that succeeded in the United States made that explicit: Make America Great Again. Culturally, this exists outside populism as well, for example in Gordon Gekko’s greed is good speech, which begins, “America has become a second-rate power.” In the late 2000s, Americans interested in transportation had to embarrassingly admit that public transit was better in Europe and East Asia, especially in its sexiest form, the high-speed trains. Musk came in and offered something Americans craved: an American way to do better, without having to learn anything about what the Europeans and Asians do. Musk himself is from South Africa, but Americans have always been more tolerant of long-settled immigrants than of foreigners.
In the era of Trump, this kind of nationalism is often characterized as the domain of the uneducated: Trump did the best among non-college-educated whites, and cut into Democratic margins with low-income whites (regardless of education). But software engineers making $120,000 a year in San Francisco or Boston are no less nationalistic – their nationalism just takes a less vulgar form. Among the tech workers themselves, technical discussions are possible; some close-mindedly respond to every criticism with “they also laughed at SpaceX,” others try to engage (e.g. Hyperloop One). But in the tech press, the response is uniformly sycophantic: Musk is a genius, offering salvation to the monolingual American, steeped in the cultural idea of the outside inventor who doesn’t need to know anything about existing technology and can substitute personal intelligence and bravery.
In reality, The Boring Company offers nothing of this sort. It is in the awkward position of being both wrong and unoriginal: unoriginal because its mission of reducing construction costs from American levels has already been achieved, and wrong because its own ideas of how to do so range from trivial to counterproductive. It has good marketing, buoyed by the tech world’s desire to believe that its internal methods and culture can solve every problem, but it has no product to speak of. What it’s selling is not just wrong, but boringly so, without any potential for salvaging its ideas for something more useful.
Tuesday, January 30, 2018
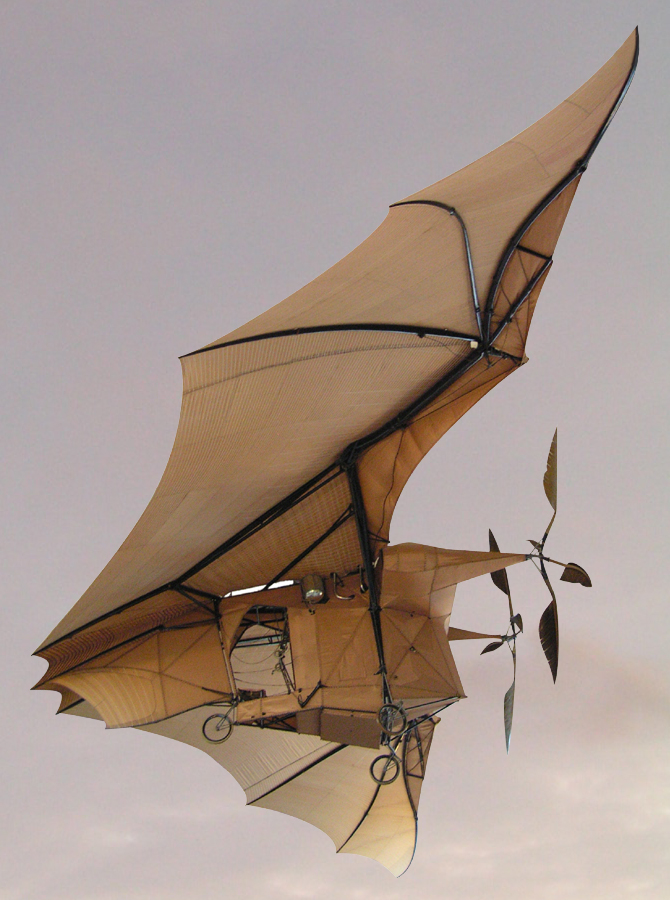
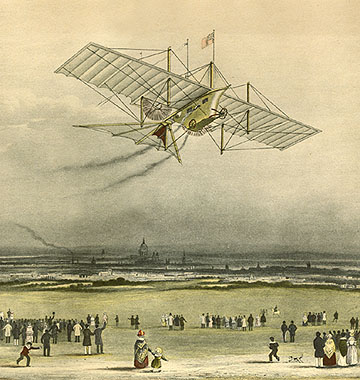
Steam-powered airplanes
I'm going to connect this up with some ongoing thread somewhere down the line, but for now I just thought I'd share this really cool list from Wikipedia of 19th-century experiments in steam-powered aircraft.
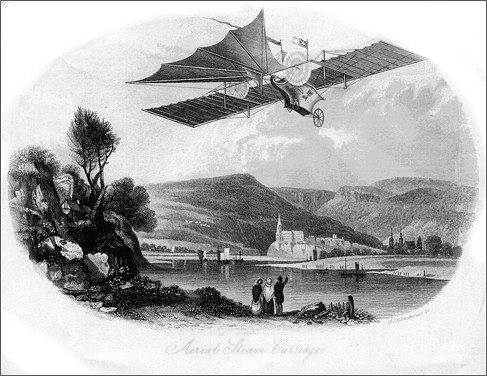
The Aerial Steam Carriage
The Henson Aerial Steam Carriage of 1843 (imaginary representation for an advertisement).
Patent drawing for the Henson Aerial Steam Carriage of 1843.
Ader Avion III
The Aerial Steam Carriage
The Henson Aerial Steam Carriage of 1843 (imaginary representation for an advertisement).
Patent drawing for the Henson Aerial Steam Carriage of 1843.
- 1842: The Aerial Steam Carriage of William Samuel Henson and John Stringfellow was patented, but was never successful, although a steam-powered model was flown in 1848.
- 1852: Henri Giffard flew a 3-horsepower (2 kW) steam-powered dirigible over Paris; it was the first powered aircraft.
- 1861 Gustave Ponton d'Amécourt made a small steam-powered craft, coining the name helicopter.
- 1874: Félix du Temple flew a steam-powered aluminium monoplane off a downhill run. While it did not achieve level flight, it was the first manned heavier-than-air powered flight.
- 1877: Enrico Forlanini built and flew a model steam-powered helicopter in Milan.
- 1882: Alexander Mozhaisky built a steam-powered plane but it did not achieve sustained flight. The engine from the plane is in the Central Air Force Museum in Monino, Moscow.
- 1890: Clément Ader built a steam-powered, bat-winged monoplane, named the Eole. Ader flew it on October 9, 1890, over a distance of 50 metres (160 ft), but the engine was inadequate for sustained and controlled flight. His flight did prove that a heavier-than-air flight was possible. Ader made at least three further attempts, the last two on 12 and 14 October 1897 for the French Ministry of War. There is controversy about whether or not he attained controlled flight. Ader did not obtain funding for his project, and that points to its probable failure.[1]
- 1894: Sir Hiram Stevens Maxim (inventor of the Maxim Gun) built and tested a large rail-mounted, steam-powered aircraft testbed, with a mass of 3.5 long tons (3.6 t) and a wingspan of 110 feet (34 m) in order to measure the lift produced by different wing configurations. The machine unexpectedly generated sufficient lift and thrust to break free of the test track and fly, but was never intended to be operated as a piloted aircraft and so crashed almost immediately owing to its lack of flight controls.
- 1896: Samuel Pierpont Langley successfully flew unpiloted steam-powered models.[2]
- 1897: Carl Richard Nyberg's Flugan developed steam-powered aircraft over a period from 1897 to 1922, but they never achieved more than a few short hops.
Ader Avion III
Monday, January 29, 2018
Tesla and the New York Times – – adding a historical component to the hype-and-bullshit tech narrative
This New York Times piece ["Tesla the Car Is a Household Name. Long Ago, So Was Nikola Tesla".
By John F. Wasik DEC. 30, 2017 ] is so bad it might actually be more useful than a better written article (such as this Smithsonian profile) would have been. Wasik provides us with an excellent example of the way writers distort and mythologize the history of technology in the service of cherished conventional narratives.
The standard tech narrative is one of great men leading us into a period of extraordinary, unprecedented progress, sometimes exciting, sometimes frightening, but always unimaginably big and just around the corner. In order to maintain this narrative, the magnitude and imminence of the recent advances is consistently overstated while the technological accomplishments and sophistication of the past is systematically understated. Credit for those advances that did happen is assigned to a handful of visionaries, many of the tragic, ahead-of-their-time variety.
These historical retcons tend to collapse quickly when held up against actual history. This is especially true here. Tesla always generated a great deal of sensationalistic coverage (more often than not intentionally), but more sober contemporary sources consistently viewed him as both a brilliant and important innovator and also an often flaky and grandiose figure, a characterization that holds up well to this day. This was the man who invented the induction motor; he was also the guy who claimed to hear interplanetary radio messages in his lab.
John F. Wasik plays the ahead-of-their-time card extensively throughout the article.
The trouble with this part of the narrative is that Tesla's Great White Whale (long-distance wireless power transmission) was simply a bad idea. It was not financially feasible because it was not feasible period. We've had over a century to consider the problem, not to mention more powerful tools and a far greater understanding of the underlying physical forces, and we can say with near absolute confidence that, even if long-distance wireless power transmission is developed in the future, it will not use Tesla's approach. No amount of funding, no degree of public support would have changed the outcome of this part of the story.
Just to be clear, even bad ideas can require brilliant engineering. That was certainly the case here, just as it was with other dead ends of the era such as mechanical televisions and steam powered aircraft. Even to this day, demonstrations of Tesla's system are impressive to watch.
Just as the if-only-he'd-had-the-money argument collapses under scrutiny, so does the lone-visionary-ahead-of-his-time narrative. If you dig through contemporary accounts, you'll find that Tesla was very much representative of the scientific and research community of his time in most ways. Both in terms of the work he was doing and the ideas he was formulating about the role of technology, he had lots of company.
Wasik consistently downplayed the work of Tesla's contemporaries, sometimes subtly (saying that the Supreme Court ruled in his favor in a 1943 patent dispute when in fact, he was one of three inventors who had their prior patents restored by the decision), sometimes in a comically over-the-top fashion as with this description of Tesla's remote-controlled torpedo.
Just to be clear, Tesla was doing important and impressive work, but as one of a number of researchers pushing the boundaries of the field of radio.
From Wikipedia:
The part about proposing the "development of torpedoes well before World War I" is even stranger. The self-propelled torpedo had been in service for more than 30 years by 1898, and remote-controlled torpedoes (using a mechanical system based on trailing cables, but still having considerable range and speed) had been in use for over 20.
It makes for a good story to credit Tesla as the lone visionary who came up with robotics and remote control by himself but was just too far ahead of his time to sell the world on that vision, but the truth is that lots of smart people were working along these lines (like Leonardo Torres y Quevedo) and pretty much everybody saw the potential value.
Tesla's ideas about remote-controlled torpedoes would take years to be implemented because it would take years for the technology to catch up with his rhetoric. You can read a very good contemporary account from scientific American that spelled out the issues.
We've talked a lot here at the blog about about the mythologizing and bullshit that are pervasive in the 21st century technology narrative. It's worth noting that those same popular but dangerously false narratives color our perception of the past as well.
By John F. Wasik DEC. 30, 2017 ] is so bad it might actually be more useful than a better written article (such as this Smithsonian profile) would have been. Wasik provides us with an excellent example of the way writers distort and mythologize the history of technology in the service of cherished conventional narratives.
The standard tech narrative is one of great men leading us into a period of extraordinary, unprecedented progress, sometimes exciting, sometimes frightening, but always unimaginably big and just around the corner. In order to maintain this narrative, the magnitude and imminence of the recent advances is consistently overstated while the technological accomplishments and sophistication of the past is systematically understated. Credit for those advances that did happen is assigned to a handful of visionaries, many of the tragic, ahead-of-their-time variety.
These historical retcons tend to collapse quickly when held up against actual history. This is especially true here. Tesla always generated a great deal of sensationalistic coverage (more often than not intentionally), but more sober contemporary sources consistently viewed him as both a brilliant and important innovator and also an often flaky and grandiose figure, a characterization that holds up well to this day. This was the man who invented the induction motor; he was also the guy who claimed to hear interplanetary radio messages in his lab.
John F. Wasik plays the ahead-of-their-time card extensively throughout the article.
He envisioned a system that could transmit not only radio but also electricity across the globe. After successful experiments in Colorado Springs in 1899, Tesla began building what he called a global “World System” near Shoreham on Long Island, hoping to power vehicles, boats and aircraft wirelessly. Ultimately, he expected that anything that needed electricity would get it from the air much as we receive transmitted data, sound and images on smartphones. But he ran out of money, and J. P. Morgan Jr., who had provided financing, turned off the spigot.
…
Tesla’s ambitions outstripped his financing. He didn’t focus on radio as a stand-alone technology. Instead, he conceived of entire systems, even if they were decades ahead of the time and not financially feasible.
Tesla failed to fully collaborate with well-capitalized industrial entities after World War I. His supreme abilities to conceptualize and create entire systems weren’t enough for business success. He didn’t manage to build successful alliances with those who could finance, build and scale up his creations.
Tesla’s achievements were awesome but incomplete. He created the A.C. energy system and the basics of radio communication and robotics but wasn’t able to bring them all to fruition. His life shows that even for a brilliant inventor, innovation doesn’t happen in a vacuum. It requires a broad spectrum of talents and skills. And lots of capital.
The trouble with this part of the narrative is that Tesla's Great White Whale (long-distance wireless power transmission) was simply a bad idea. It was not financially feasible because it was not feasible period. We've had over a century to consider the problem, not to mention more powerful tools and a far greater understanding of the underlying physical forces, and we can say with near absolute confidence that, even if long-distance wireless power transmission is developed in the future, it will not use Tesla's approach. No amount of funding, no degree of public support would have changed the outcome of this part of the story.
Just to be clear, even bad ideas can require brilliant engineering. That was certainly the case here, just as it was with other dead ends of the era such as mechanical televisions and steam powered aircraft. Even to this day, demonstrations of Tesla's system are impressive to watch.
[Tesla understood the value of celebrity.]
Just as the if-only-he'd-had-the-money argument collapses under scrutiny, so does the lone-visionary-ahead-of-his-time narrative. If you dig through contemporary accounts, you'll find that Tesla was very much representative of the scientific and research community of his time in most ways. Both in terms of the work he was doing and the ideas he was formulating about the role of technology, he had lots of company.
Wasik consistently downplayed the work of Tesla's contemporaries, sometimes subtly (saying that the Supreme Court ruled in his favor in a 1943 patent dispute when in fact, he was one of three inventors who had their prior patents restored by the decision), sometimes in a comically over-the-top fashion as with this description of Tesla's remote-controlled torpedo.
Shortly after filing a patent application in 1897 for radio circuitry, Tesla built and demonstrated a wireless, robotic boat at the old Madison Square Garden in 1898 and, again, in Chicago at the Auditorium Theater the next year. These were the first public demonstrations of a remote-controlled drone.
An innovation in the boat’s circuitry — his “logic gate” — became an essential steppingstone to semiconductors. [This is a somewhat controversial claim. We'll try to come back to this later – MP]
Tesla’s tub-shaped, radio-controlled craft heralded the birth of what he called a “teleautomaton”; later, the world would settle on the word robot. We can see his influence in devices ranging from “smart” speakers like Amazon’s Echo to missile-firing drone aircraft.
Tesla proposed the development of torpedoes well before World War I. These weapons eventually emerged in another form — launched from submarines.
Just to be clear, Tesla was doing important and impressive work, but as one of a number of researchers pushing the boundaries of the field of radio.
From Wikipedia:
In 1894, the first example of wirelessly controlling at a distance was during a demonstration by the British physicist Oliver Lodge, in which he made use of a Branly's coherer to make a mirror galvanometer move a beam of light when an electromagnetic wave was artificially generated. This was further refined by radio innovators Guglielmo Marconi and William Preece, at a demonstration that took place on December 12, 1896, at Toynbee Hall in London, in which they made a bell ring by pushing a button in a box that was not connected by any wires. In 1898 Nikola Tesla filed his patent, U.S. Patent 613,809, named Method of an Apparatus for Controlling Mechanism of Moving Vehicle or Vehicles, which he publicly demonstrated by radio-controlling a boat during an electrical exhibition at Madison Square Garden. Tesla called his boat a "teleautomaton"
The part about proposing the "development of torpedoes well before World War I" is even stranger. The self-propelled torpedo had been in service for more than 30 years by 1898, and remote-controlled torpedoes (using a mechanical system based on trailing cables, but still having considerable range and speed) had been in use for over 20.
It makes for a good story to credit Tesla as the lone visionary who came up with robotics and remote control by himself but was just too far ahead of his time to sell the world on that vision, but the truth is that lots of smart people were working along these lines (like Leonardo Torres y Quevedo) and pretty much everybody saw the potential value.
Tesla's ideas about remote-controlled torpedoes would take years to be implemented because it would take years for the technology to catch up with his rhetoric. You can read a very good contemporary account from scientific American that spelled out the issues.
We've talked a lot here at the blog about about the mythologizing and bullshit that are pervasive in the 21st century technology narrative. It's worth noting that those same popular but dangerously false narratives color our perception of the past as well.
Friday, January 26, 2018
Add Adam Conover to the list of replication bullies
[Spelling error corrected.]
Most people in the news media missed the joke when Jon Stewart took over the Daily Show, or, more accurately, saw a joke that wasn't there. It took them a while to realize that while Stewart, the cast, and the writers of the show were trying to be funny, they generally weren't kidding.
The Daily Show was in that sense a very serious response to the disastrous state of turn-of-the-millennium journalism. As bad as things are now, it is easy to forget how much worse they were in the period roughly defined by Whitewater, Bush V Gore, and build-up to the Iraq war. The best of the new voices, such as Josh Marshall, were just beginning to be heard. The New York Times was pretty much the same, but now its devotion to practices like false balance, blind adherence to conventional narratives, and Clinton derangement syndrome have grown increasingly controversial with the rest of the media with papers like the Washington Post aggressively pushing back. In 1999, the rest of the press corps was seeing who could be the most like the NYT rather than criticizing it.
When the true nature of Stewart's Daily Show finally began to dawn on people, there was considerable bad feeling among journalists, lots of grumbling that Stewart, Colbert, and the rest had forgotten their place. Colbert's performance at the White House Correspondents' Dinner in particular hit a huge nerve. The people in that ball room were perhaps the last to realize that the satirical bits were driven by genuine contempt for a profession that had gone to hell.
Stewart and Colbert focused on press criticism because it was a ripe target for satire but also because it was something that needed to be done (God knows hacks like David Carr and Jack Shafer were not up to the job). The next generation, John Oliver, Samantha Bee, and in his new role, Stephen Colbert have shifted more toward news presented with a satirical bent once again filling in gaps left by conventional journalism.
Go forward another iteration (and another literal generation) and you get Cracked and College Humor who have taken those same basic instincts and applied them to less topical subjects, often focusing more on education than news.
One common thread that runs through all of the shows over the past almost 20 years is a reaction against the polite toleration of bullshit that it come to dominate mainstream journalism. It is worth noting that Adam Conover squarely placed himself in the pro-replication camp and has made citing sources and acknowledging errors a prominent part of Adam Ruins Everything.
Most people in the news media missed the joke when Jon Stewart took over the Daily Show, or, more accurately, saw a joke that wasn't there. It took them a while to realize that while Stewart, the cast, and the writers of the show were trying to be funny, they generally weren't kidding.
The Daily Show was in that sense a very serious response to the disastrous state of turn-of-the-millennium journalism. As bad as things are now, it is easy to forget how much worse they were in the period roughly defined by Whitewater, Bush V Gore, and build-up to the Iraq war. The best of the new voices, such as Josh Marshall, were just beginning to be heard. The New York Times was pretty much the same, but now its devotion to practices like false balance, blind adherence to conventional narratives, and Clinton derangement syndrome have grown increasingly controversial with the rest of the media with papers like the Washington Post aggressively pushing back. In 1999, the rest of the press corps was seeing who could be the most like the NYT rather than criticizing it.
When the true nature of Stewart's Daily Show finally began to dawn on people, there was considerable bad feeling among journalists, lots of grumbling that Stewart, Colbert, and the rest had forgotten their place. Colbert's performance at the White House Correspondents' Dinner in particular hit a huge nerve. The people in that ball room were perhaps the last to realize that the satirical bits were driven by genuine contempt for a profession that had gone to hell.
Stewart and Colbert focused on press criticism because it was a ripe target for satire but also because it was something that needed to be done (God knows hacks like David Carr and Jack Shafer were not up to the job). The next generation, John Oliver, Samantha Bee, and in his new role, Stephen Colbert have shifted more toward news presented with a satirical bent once again filling in gaps left by conventional journalism.
Go forward another iteration (and another literal generation) and you get Cracked and College Humor who have taken those same basic instincts and applied them to less topical subjects, often focusing more on education than news.
One common thread that runs through all of the shows over the past almost 20 years is a reaction against the polite toleration of bullshit that it come to dominate mainstream journalism. It is worth noting that Adam Conover squarely placed himself in the pro-replication camp and has made citing sources and acknowledging errors a prominent part of Adam Ruins Everything.
Thursday, January 25, 2018
A Turn of the Century Childhood's End
This may go against conventional wisdom, but what we now call New Age beliefs (normally seen as children of the counter-culture) are largely a product of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Parapsychology? Check. Ghosts and similar entities? Check. Fascination with paganism and arcane religions? Check. Space aliens? Check. And finally, the idea that humanity is on the verge of a huge evolutionary leap, a leap that might already be happening? Check.
The turn of the century probably also marked the peak respectability for these beliefs. It's difficult imagining something like this running in Scientific American in the 21sst century.
The turn of the century probably also marked the peak respectability for these beliefs. It's difficult imagining something like this running in Scientific American in the 21sst century.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)






_-_Scientific_American_1898.jpg)