I've heard the argument that unemployment benefits caused higher unemployment before, but I never expected anyone to use Germany's relatively strong numbers to support the case.
Comments, observations and thoughts from two bloggers on applied statistics, higher education and epidemiology. Joseph is an associate professor. Mark is a professional statistician and former math teacher.
Tuesday, August 16, 2011
Last conference of the year
And so posting on my end is light this week. I'll have new content this weekend, though.
Friday, August 12, 2011
Noah Smith has some smart things to say about libertarians and property rights...
...and you should probably read the whole thing, but I wanted to single out this passage:
That's right: irreducible transaction costs are a fly in the libertarian soup. Completing an economic transaction, however quick and easy, involves some psychological cost; you have to consider whether the transaction is worth it (optimization costs), and you have to suffer the small psychological annoyance that all humans feel each time money leaves their bank account (the same phenomenon contributes to loss aversion and money illusion). Past a certain point, the gains to privatization are outweighed by the sheer weight of transaction cost externalities. (Note that transaction costs also kill the Coase Theorem, another libertarian standby; this is no coincidence.)This dovetails nicely with this discussion about why the decision-making processes of engineers and scientists are often 'irrational' in the strict economics sense of the word. Like transactions, decision-making algorithms have a cost. In most cases, these costs are fairly small (like the few seconds it takes to decide on a brand of beer) and you can get away with ignoring them, but freshwater economists routinely make arguments for rational behavior that require people to make incredibly complicated calculations almost instantly. What's worse, they continue to make these arguments even when data suggests that people are using other, simpler rules to make their decisions.
Stop by and see what you think
Andrew Gelman has some intriguing news about the possibility of reform in the institutional review board system.
A sentence that you just don't want to hear
Matt Yglesias was writing about an innovative program in the Netherlands when he made the comment:
At the time, I mentioned it to Mark (my co-blogger) as one of those sentences that you just don't want to have applied to your country, even in jest. Now Jeffrey Early is willing to ask when was the last time that the United States was a policy innovator. His depressing suggestion is back when Richard Nixon was president.
So here is my question to the blogosphere: what can the United States do to go back to being a leader in policy innovation?
[My own angle is to look at work being done at places like The Incidental Economist to see if we can possibly find an alternative way forward for Health Care Policy]
At this point, it just strikes me as fundamentally unlikely that bold policy innovation is going to come out of the sclerotic United States.
At the time, I mentioned it to Mark (my co-blogger) as one of those sentences that you just don't want to have applied to your country, even in jest. Now Jeffrey Early is willing to ask when was the last time that the United States was a policy innovator. His depressing suggestion is back when Richard Nixon was president.
So here is my question to the blogosphere: what can the United States do to go back to being a leader in policy innovation?
[My own angle is to look at work being done at places like The Incidental Economist to see if we can possibly find an alternative way forward for Health Care Policy]
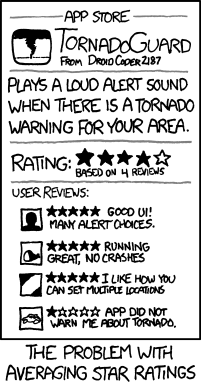
XKCD
Thursday, August 11, 2011
You might not want to read it while you're eating...
But you really should read Michael Lewis' latest entry. It's one of the best things you'll read on the German economy and almost certainly the only article you'll find describing the country's financial system through scatological metaphors (no, really).
Tuesday, August 9, 2011
Must-reads
Nate Silver and Felix Salmon take very different views on S&P. I don't know who I'd call the winner -- Silver's case seems slightly more convincing, but Salmon's opinions in these matters carry a lot of weight -- but both pieces are well worth your time.
I think we can all use a distraction now
Which is why the long delayed return of Burn Notice to Hulu is such welcome news to those of us without cable.
Tax Policy
From John Quiggin:
This is actually a very constructive addition to the discussion of how to finance government and society in general. When I was growing up, the general idea we had was that serious tax cuts had to focus on the middle class because that was where all of the money was. But 25% of the national income is a lot and it isn't clear that this type of extreme inequality is socially useful. Few people seem to suggest that we should impoverish the rich, but would it be a horrible world where the top 1% had 15% of the post-tax income?
The wealth that has accrued to those in the top 1 per cent of the US income distribution is so massive that any serious policy program must begin by clawing it back.
If their 25 per cent, or the great bulk of it, is off-limits, then it’s impossible to see any good resolution of the current US crisis. It’s unsurprising that lots of voters are unwilling to pay higher taxes, even to prevent the complete collapse of public sector services. Median household income has been static or declining for the past decade, household wealth has fallen by something like 50 per cent (at least for ordinary households whose wealth, if they have any, is dominated by home equity) and the easy credit that made the whole process tolerable for decades has disappeared. In these circumstances, welshing on obligations to retired teachers, police officers and firefighters looks only fair.
In both policy and political terms, nothing can be achieved under these circumstances, except at the expense of the top 1 per cent. This is a contingent, but inescapable fact about massively unequal, and economically stagnant, societies like the US in 2010. By contrast, in a society like that of the 1950s and 1960s, where most people could plausibly regard themselves as middle class and where middle class incomes were steadily rising, the big questions could be put in terms of the mix of public goods and private income that was best for the representative middle class citizen. The question of how much (more) to tax the very rich was secondary – their share of national income was already at an all time low.
This is actually a very constructive addition to the discussion of how to finance government and society in general. When I was growing up, the general idea we had was that serious tax cuts had to focus on the middle class because that was where all of the money was. But 25% of the national income is a lot and it isn't clear that this type of extreme inequality is socially useful. Few people seem to suggest that we should impoverish the rich, but would it be a horrible world where the top 1% had 15% of the post-tax income?
Monday, August 8, 2011
Bad optics
I'm sure there's nothing sinister going on here, but S&P certainly has a gift for looking bad (from Marketplace):
This final note today, in which S&P beats up on Warren Buffet. The billionaire went on CNBC this morning, said he wasn’t worried at all about the debt downgrade and said, in fact, that the downgrade changed his opinion of S&P — not his opinion of U.S. Treasuries.Funnily enough, couple of hours later, S&P put Buffett’s company Berkshire Hathaway on notice for a possible downgrade.
Hmmm.
Also, we should note here: Berkshire Hathaway’s the single biggest shareholder in S&P’s competitor, Moody’s.
Libertarianism and it's limitations
I have long held that the weak underbelly of libertarian theory (in the modern form) is how to justify current wealth distributions (and thus hold current property rights inviolate). Brad DeLong does a good job of laying out the mental steps required:
It is step 11 that seems to be the most interesting to me. Nobody really wants to argue for anarchy but that doesn't mean that pools of wealth are good, either. I suspect a false dichotomy is present as other options exist as well.
Furthermore, the system also ignores the influence of wealth on process. Differences in prestige, corruption and credibility can lead to issues with step 5, as well. So I think we need to be careful about making property rights primary. Obviously ownership has important effects in making a specific person responsible for an item (otherwise you can get the "Tragedy of the Commons" issues). But that effect works best on small pieces of property that are directly used by the person (a car, a house, a factory) and seem to become less helpful on larger scales (like in a corporation where you need to hire a management team who then bring in principal agent concerns).
Definitely something to consider.
Well, let me sketch out the logic of Robert Nozick's argument for his version of catallaxy as the only just order. It takes only fourteen steps:
1. Nobody is allowed to make utilitarian or consequentialist arguments. Nobody.
2. I mean it: utilitarian or consequentialist arguments--appeals to the greatest good of the greatest number or such--are out-of-order, completely. Don't even think of making one.
3. The only criterion for justice is: what's mine is mine, and nobody can rightly take or tax it from me.
4. Something becomes mine if I make it.
5. Something becomes mine if I trade for it with you if it is yours and if you are a responsible adult.
6. Something is mine if I take it from the common stock of nature as long as I leave enough for latecomers to also take what they want from the common stock of nature.
7. But now everything is owned: the latecomers can't take what they want.
8. It gets worse: everything that is mine is to some degree derived from previous acts of original appropriation--and those were all illegitimate, since they did not leave enough for the latecomers to take what they want from the common stock of nature.
9. So none of my property is legitimate, and nobody I trade with has legitimate title to anything.
10. Oops.
11. I know: I will say that the latecomers would be poorer under a system of propertyless anarchy in which nobody has a right to anything than they are under my system--even though others have gotten to appropriate from nature and they haven't.
12.Therefore they don't have a legitimate beef: they are advantaged rather than disadvantaged by my version of catallaxy, and have no standing to complain.
13. Therefore everything mine is mine, and everything yours is yours, and how dare anybody claim that taxing anything of mine is legitimate!
14. Consequentialist utilitarian argument? What consequentialist utilitarian argument?
To be able to successfully explain Nozickian political philosophy is to face the reality that it is self-parody, or perhaps CALVINBALL!
It is step 11 that seems to be the most interesting to me. Nobody really wants to argue for anarchy but that doesn't mean that pools of wealth are good, either. I suspect a false dichotomy is present as other options exist as well.
Furthermore, the system also ignores the influence of wealth on process. Differences in prestige, corruption and credibility can lead to issues with step 5, as well. So I think we need to be careful about making property rights primary. Obviously ownership has important effects in making a specific person responsible for an item (otherwise you can get the "Tragedy of the Commons" issues). But that effect works best on small pieces of property that are directly used by the person (a car, a house, a factory) and seem to become less helpful on larger scales (like in a corporation where you need to hire a management team who then bring in principal agent concerns).
Definitely something to consider.
Jonathan Chait: "I suppose I didn't express myself as well as I could have." -- repeatedly
Jonathan Chait today dismissed this objection (also discussed by Andrew Gelman) that being easily fired really isn't really part of the definition of a professional with the line:
I think Palko's point is pretty obviously just wordplay, but I suppose I didn't express myself as well as I could have.Normally I'd let it rest there (it was one of the more trivial objections I've raised about Chait's position on education), but we really ought to note that this is not the first time we've seen this line:
But being "treated like professionals" has to mean both the opportunity to earn a good living if you do well and the potential to be fired if you fail.You can find the full context of that line and my reaction to it here.
My disconnect with Jon Chait
Let me begin with Jon Chait being one of my favorite writers, a must-read, and a person with whom I agree > 90% of the time. I think that the one area we really differ is with teaching:
I think I can put my finger on the point of disconnection here. I would gladly take employment In which hard work and results were rewarded (and people who were bad fits were quietly eased out of the profession). These are my favorite work places, as I never want to be in a role where I am not contributing in a substantive way.
But what I think worries me about the attack on teacher tenure is that it seems to be coupled with a small government/austerity movement. I worry that the endgame is no tenure and less compensation (regardless of performance). That approach would open up higher education to worse incentives than it has now and increase the pressure for a parallel (and private) system. Looking at the cost of higher education, my concern is that the poor might be priced out of the education market.
I might be wrong about this pattern, but many countries have balanced job security with quality education (e.g. Canada, Sweden, Finland). I am not against a new pathway, I am just not sure how to increase compensation (to balance against the loss of job security) in the current environment. But I note that Jon Chait is coupling increased compensation opportunities with decreased job security. A reasonable trade, so long as it doesn't fall victim to the desperate need to shrink government that is in the very air these days.
If there is a path forward, I would actually be happy to revisit this question in a positive way. But why is this a burning question in the middle of a period of austerity budgets when it is unclear where the revenue for such reforms would come from?
I think Palko's point is pretty obviously just wordplay, but I suppose I didn't express myself as well as I could have. Being a professional, to most people, means having the opportunity to gain higher pay and recognition with greater success. Such a system also, almost inevitably, entails the possibility of having some consequences for failure. Teaching is very different than most career paths open to college graduates in that it protects its members from firing even in the case of gross incompetence, and it largely denies them the possibility to rise quickly if they demonstrate superior performance.
Obviously the realistic possibility of being fired for gross incompetence would not in and of itself do much to attract more highly qualified teachers, but the opportunity to receive performance-differentiated pay would.
I think I can put my finger on the point of disconnection here. I would gladly take employment In which hard work and results were rewarded (and people who were bad fits were quietly eased out of the profession). These are my favorite work places, as I never want to be in a role where I am not contributing in a substantive way.
But what I think worries me about the attack on teacher tenure is that it seems to be coupled with a small government/austerity movement. I worry that the endgame is no tenure and less compensation (regardless of performance). That approach would open up higher education to worse incentives than it has now and increase the pressure for a parallel (and private) system. Looking at the cost of higher education, my concern is that the poor might be priced out of the education market.
I might be wrong about this pattern, but many countries have balanced job security with quality education (e.g. Canada, Sweden, Finland). I am not against a new pathway, I am just not sure how to increase compensation (to balance against the loss of job security) in the current environment. But I note that Jon Chait is coupling increased compensation opportunities with decreased job security. A reasonable trade, so long as it doesn't fall victim to the desperate need to shrink government that is in the very air these days.
If there is a path forward, I would actually be happy to revisit this question in a positive way. But why is this a burning question in the middle of a period of austerity budgets when it is unclear where the revenue for such reforms would come from?
Another This American Life episode you ought to listen to...
Unless you heard it the first time it ran. The title is "Million Dollar Idea" and it has two stories of interest to OE readers, one on MIT's elevator pitch contest and another memorable piece on the treacherous water of medical PR. On top of that you get an incredible story of a man who figured out a way to rig a game show without actually cheating and the origin of the phrase "the heroin's doing the heavy lifting."
The download is free for the next few days, but you should throw them a few bucks if you can spare it. They do good work.
The download is free for the next few days, but you should throw them a few bucks if you can spare it. They do good work.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)