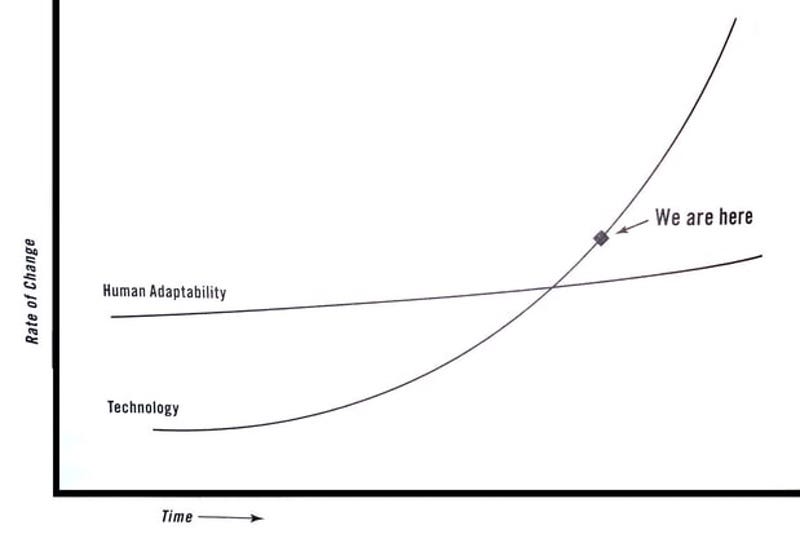
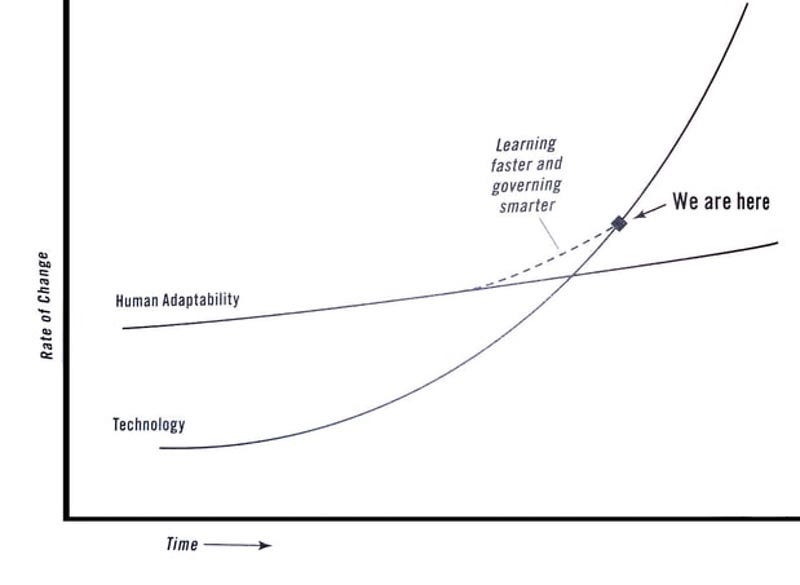
DYING METAPHORS. A newly invented metaphor assists thought by evoking a visual image, while on the other hand a metaphor which is technically ‘dead’ (e. g. iron resolution) has in effect reverted to being an ordinary word and can generally be used without loss of vividness. But in between these two classes there is a huge dump of worn-out metaphors which have lost all evocative power and are merely used because they save people the trouble of inventing phrases for themselves. Examples are: Ring the changes on, take up the cudgel for, toe the line, ride roughshod over, stand shoulder to shoulder with, play into the hands of, no axe to grind, grist to the mill, fishing in troubled waters, on the order of the day, Achilles’ heel, swan song, hotbed. Many of these are used without knowledge of their meaning (what is a ‘rift’, for instance?), and incompatible metaphors are frequently mixed, a sure sign that the writer is not interested in what he is saying. Some metaphors now current have been twisted out of their original meaning without those who use them even being aware of the fact. For example, toe the line is sometimes written as tow the line. Another example is the hammer and the anvil, now always used with the implication that the anvil gets the worst of it. In real life it is always the anvil that breaks the hammer, never the other way about: a writer who stopped to think what he was saying would avoid perverting the original phrase.We've been heading toward this for a long time. From the beginning, the idea of disruption never explained nearly as much as it was supposed to. There were always as many exceptions as cases and much of the appeal of the idea could be attributed to the way it played into popular narratives about visionary innovators.
George Orwell
By now, the term has been so overused that it has lost all meaning. Here's Jill Lepore writing for the New Yorker.
Ever since “The Innovator’s Dilemma,” everyone is either disrupting or being disrupted. There are disruption consultants, disruption conferences, and disruption seminars. This fall, the University of Southern California is opening a new program: “The degree is in disruption,” the university announced. “Disrupt or be disrupted,” the venture capitalist Josh Linkner warns in a new book, “The Road to Reinvention,” in which he argues that “fickle consumer trends, friction-free markets, and political unrest,” along with “dizzying speed, exponential complexity, and mind-numbing technology advances,” mean that the time has come to panic as you’ve never panicked before. Larry Downes and Paul Nunes, who blog for Forbes, insist that we have entered a new and even scarier stage: “big bang disruption.” “This isn’t disruptive innovation,” they warn. “It’s devastating innovation.”
Obviously, sense has been draining away for a long time, but the term officially flat-lined when the heads of AT&T and Time Warner headed to DC to defend the indefensible. From the must-read Gizmodo piece by Michael Nunez.
In front of the Senate subcommittee today, AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson brazenly dismissed concerns of potentially anticompetitive behavior. The bespectacled executive, according to a New York Times report, told lawmakers that the merger would “disrupt the entrenched pay-TV models” and give customers more options.
The truth is a little more complicated than that. AT&T is already the second-largest US telecommunications company (with 133.3 million subscribers) and the largest pay-TV service in the US and the world. If it merged with Time Warner, the second-largest broadband provider and third-largest video provider in the US, it would create a media conglomerate with unspeakable power. Critics say it would be a conglomerate that many companies just couldn’t compete with.
We are truly into Newspeak territory here. The sole purpose of this type of mergers is to entrench position and prevent the industry from being disrupted. Those at the top quite accurately view disruption as a serious and possibly existential threat to the status quo. If you can now use the term to describe a mega-merger, it has no meaning left at all.